Interventional Radiology
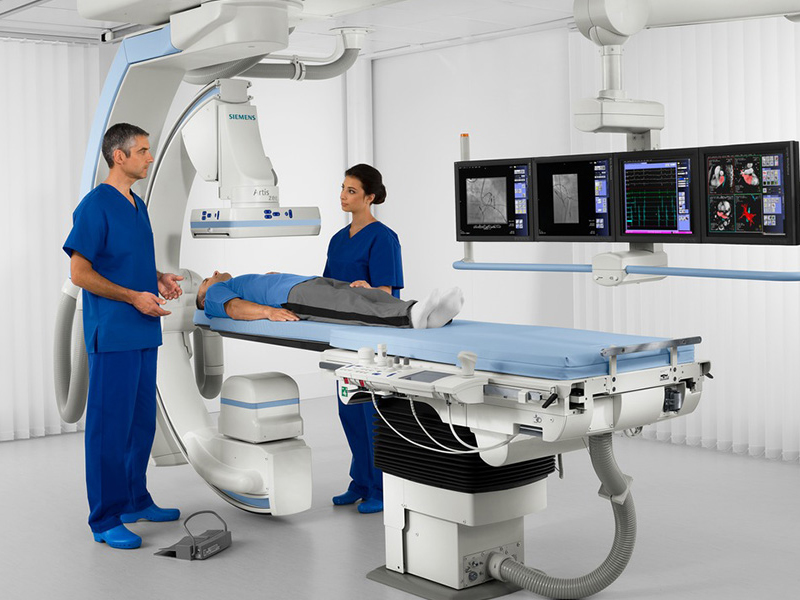
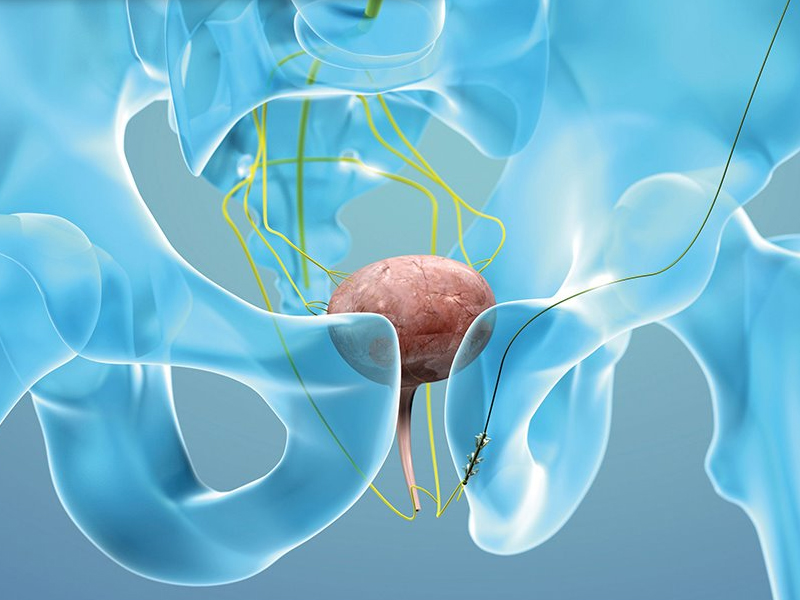
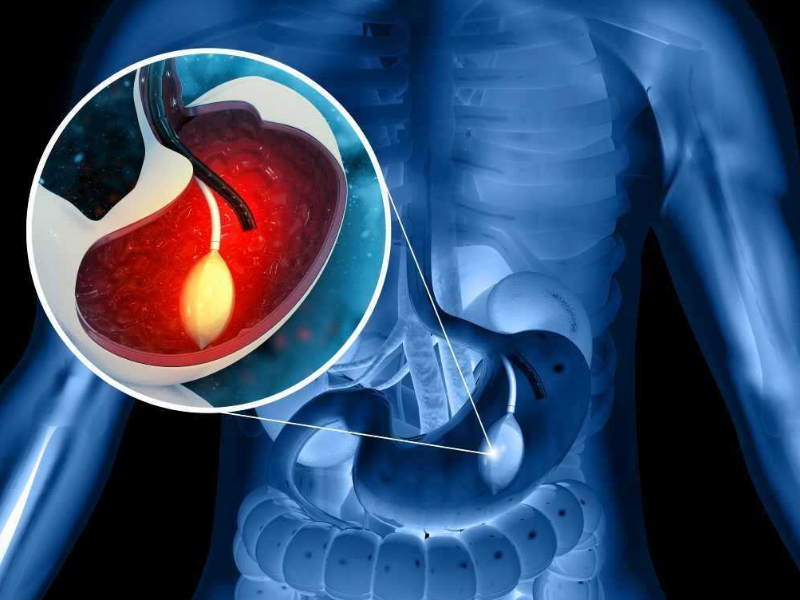
Interventional radiology is a medical sub-branch that intervenes in the diagnosis and treatment of diseases with minimally invasive methods using imaging methods. In this branch of medicine, radiologists perform treatment or diagnostic interventions by guiding thin catheters or needles into the body with the help of imaging techniques.
Interventional radiology can be a less invasive and often less traumatic option for patients than open surgical interventions. Radiologists determine the location and extent of the disease using imaging techniques such as x-ray, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), computed tomography (CT) or ultrasonography, and perform interventional procedures with the help of this imaging.
Interventional radiology includes many procedures such as placing stents in blood vessels, angioplasty, embolization (blocking vessels), tumor ablation (destruction of tumors), biopsy (sampling), drainage applications and vertebralplasty. These techniques provide effective and successful results in the treatment of various medical conditions such as cancer, blockages in blood vessels, kidney and liver diseases. Interventional radiology makes significant contributions to medical treatment processes by enabling patients to recover faster and experience fewer complications. Additionally, it increases the diversity of healthcare services by offering alternative treatment options to patients who are not suitable for surgical intervention. Interventional radiologists strive to best evaluate and treat patients’ health conditions by using imaging techniques and advanced treatment methods.